leetCode热题40-45 解题代码,调试代码和思路
# 前言本文属于特定的六道题目题解和调试代码。
1 ✔ 爬楼梯 Easy 2023-03-24 107
2 ✔ 排序链表 Medium 2022-12-13 106
3 ✔ 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II Medium 2023-03-18 105
4 ✔ 下一个排列 Medium 2023-02-15 105
5 ✔ 最长公共子序列 Medium 2023-03-23 104
6 ✔ 两数相加 Medium 2023-03-22 102
正所谓磨刀不误砍柴功。下面我做这几篇文档对于涉及的题型或者数据结构的分析都很有帮助,贴出来仅供参考。
[如何调试递归程序,有何技巧?](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44850489/article/details/129528264)
[按照树形结构直观地打印出一棵二叉树、快速创建leetcode中树的结构(Java)](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44850489/article/details/129557959)
---
@(leetCode热题40-45 解题代码,调试代码和思路)
# 1 ✔ 爬楼梯 Easy 2023-03-24 107
//假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
//
// 每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
//
//
//
// 示例 1:
//
//
//输入:n = 2
//输出:2
//解释:有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
//1. 1 阶 + 1 阶
//2. 2 阶
//
// 示例 2:
//
//
//输入:n = 3
//输出:3
//解释:有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
//1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
//2. 1 阶 + 2 阶
//3. 2 阶 + 1 阶
//
//
//
//
// 提示:
//
//
// 1 <= n <= 45
//
//
// Related Topics 记忆化搜索 数学 动态规划 👍 2945 👎 0
---
>自测代码
```java
public class P70_ClimbingStairs{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试代码
Solution solution = new P70_ClimbingStairs().new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.climbStairs(4));
}
//力扣代码
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (0 >= n) {
return 0;
}
if (1 == n) {
return 1;
}
if (2 == n) {
return 2;
}
int l = 1;
int r = 2;
int temp = l+r;
for (int i = 3; i < n; i++) {
temp = l+r;
l = r;
r = temp;
}
return l+r;
}
}
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
}
```
> 提交代码
```java
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (0 >= n) {
return 0;
}
if (1 == n) {
return 1;
}
if (2 == n) {
return 2;
}
int l = 1;
int r = 2;
int temp = l+r;
for (int i = 3; i < n; i++) {
temp = l+r;
l = r;
r = temp;
}
return l+r;
}
}
```
# 2 ✔ 排序链表 Medium 2022-12-13 106
>//给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
//
//
//
//
//
//
// 示例 1:
//
//
//输入:head =
//输出:
//
//
// 示例 2:
//
//
//输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
//输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
//
//
// 示例 3:
//
//
//输入:head = []
//输出:[]
//
//
//
//
// 提示:
//
//
// 链表中节点的数目在范围 内
// -10⁵ <= Node.val <= 10⁵
//
//
//
//
// 进阶:你可以在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
//
// Related Topics 链表 双指针 分治 排序 归并排序 👍 1952 👎 0
---
有去写了一种方式:就是从头开始向后一次一个添加进来排序,但是显示超时了。
疑惑点:如果使用归并排序,分治,应该需要知道中位数,但是遍历的时间不就是n了?之后再回溯 合并两个链表时,时间应该也是n
解决方案:这道题目采用了一种非常新颖的方式,首先是通过`位运算` 将需要排序的子链表长度控制在 1 2 4 8... ,第一遍是将所有相邻的两个排序,然后连接,然后将相邻的四个排序连接。最后得出所有的排序连接。
`需要注意的就是整个过程中关键节点的赋值。`
链表的解题思路,就是找关键节点,可以先声明出来, 再就是双指针。
先新建一个dummyHead 做链表开头。
然后新建一个 pre 做需要排序的前半部分的最后一个节点
再新建一个cuur 做遍历节点。
head1,head2做要排序的两个链表的的头节点
> 自测代码
```java
public class P148_SortList{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试代码
Solution solution = new P148_SortList().new Solution();
/*想到的解决方法:遍历两个指针,l指针及之前的都是排序完成的,r为要插入的指针*/
/*如果使用归并排序,分治,应该需要知道中位数,但是遍历的时间不就是n了?之后再回溯合并两个链表时,时间应该也是n*/
/*解决方案:就是上面疑惑的解决方法*/
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode("[-1,5,3,4,0]");
ListNode listNode = solution.sortList(listNode1);
System.out.println(listNode.toString());
}
//力扣代码
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
int len = 0 ;
ListNode sum = head;
while (sum != null) {
len++;
sum = sum.next;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
for (int i = 1; i < len ; i <<= 1) {
ListNode pre = dummyHead,curr = dummyHead.next;
while (curr != null){
ListNode head1 = curr;
for (int i1 = 1; i1 < i && curr.next != null; i1++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode head2 = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
curr = head2;
for (int i1 = 1; i1 < i && curr != null && curr.next != null; i1++) {
curr= curr.next;
}
ListNode next = null;
if (curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
}
ListNode merge = merge(head1, head2);
pre.next = merge;
while (pre.next != null) {
pre = pre.next;
}
curr = next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode listNode = dummyHead;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.val > head2.val) {
listNode.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
listNode = listNode.next;
}else {
listNode.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
if (head1 == null) {
listNode.next = head2;
}else {
listNode.next = head1;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
}
```
>提交代码
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
int len = 0 ;
ListNode sum = head;
while (sum != null) {
len++;
sum = sum.next;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
for (int i = 1; i < len ; i <<= 1) {
ListNode pre = dummyHead,curr = dummyHead.next;
while (curr != null){
ListNode head1 = curr;
for (int i1 = 1; i1 < i && curr.next != null; i1++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode head2 = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
curr = head2;
for (int i1 = 1; i1 < i && curr != null && curr.next != null; i1++) {
curr= curr.next;
}
ListNode next = null;
if (curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
}
ListNode merge = merge(head1, head2);
pre.next = merge;
while (pre.next != null) {
pre = pre.next;
}
curr = next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode listNode = dummyHead;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.val > head2.val) {
listNode.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
listNode = listNode.next;
}else {
listNode.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
if (head1 == null) {
listNode.next = head2;
}else {
listNode.next = head1;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
```
# 3 ✔ 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II Medium 2023-03-18 105
>//给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除原始链表中所有重复数字的节点,只留下不同的数字 。返回 已排序的链表 。
//
//
//
// 示例 1:
//
//
//输入:head =
//输出:
//
//
// 示例 2:
//
//
//输入:head =
//输出:
//
//
//
//
// 提示:
//
//
// 链表中节点数目在范围 内
// -100 <= Node.val <= 100
// 题目数据保证链表已经按升序 排列
//
//
// Related Topics 链表 双指针 👍 1090 👎 0
---
这道题目相对于上道题目我觉得难度不大,把上道题目中的找关键节点搞懂,我觉得这道题目就很好解决。
>自测代码
```java
public class P82_RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedListIi{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试代码
Solution solution = new P82_RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedListIi().new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.deleteDuplicates(new ListNode("")).toString());
}
//力扣代码
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode pre = dummyHead;
ListNode cuur = dummyHead.next;
while (cuur != null &&cuur.next != null ) {
if (cuur.val == cuur.next.val) {
while (cuur != null &&cuur.next != null && cuur.val == cuur.next.val) {
cuur.next = cuur.next.next;
}
cuur = cuur.next;
pre.next = cuur;
}else {
pre = pre.next;
cuur = cuur.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
}
```
> 提交代码
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode pre = dummyHead;
ListNode cuur = dummyHead.next;
while (cuur != null &&cuur.next != null ) {
if (cuur.val == cuur.next.val) {
while (cuur != null &&cuur.next != null && cuur.val == cuur.next.val) {
cuur.next = cuur.next.next;
}
cuur = cuur.next;
pre.next = cuur;
}else {
pre = pre.next;
cuur = cuur.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
```
# 4 ✔ 下一个排列 Medium 2023-02-15 105
//整数数组的一个 排列 就是将其所有成员以序列或线性顺序排列。
//
//
// 例如,arr = ,以下这些都可以视作 arr 的排列:、、、 。
//
//
// 整数数组的 下一个排列 是指其整数的下一个字典序更大的排列。更正式地,如果数组的所有排列根据其字典顺序从小到大排列在一个容器中,那么数组的 下一个排列 就
//是在这个有序容器中排在它后面的那个排列。如果不存在下一个更大的排列,那么这个数组必须重排为字典序最小的排列(即,其元素按升序排列)。
//
//
// 例如,arr = 的下一个排列是 。
// 类似地,arr = 的下一个排列是 。
// 而 arr = 的下一个排列是 ,因为 不存在一个字典序更大的排列。
//
//
// 给你一个整数数组 nums ,找出 nums 的下一个排列。
//
// 必须 原地 修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
//
//
//
// 示例 1:
//
//
//输入:nums =
//输出:
//
//
// 示例 2:
//
//
//输入:nums =
//输出:
//
//
// 示例 3:
//
//
//输入:nums =
//输出:
//
//
//
//
// 提示:
//
//
// 1 <= nums.length <= 100
// 0 <= nums <= 100
//
//
// Related Topics 数组 双指针 👍 2124 👎 0
---
疑惑点:题没有读懂,字典排序如果都是数字,类似于看组合的数字大小。
分析题目发现,就是找到最后一个数字 和从后往前第一个比它小的数字交换,然后对中间的数字进行排序。
>自测代码
```java
public class P31_NextPermutation{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试代码
Solution solution = new P31_NextPermutation().new Solution();
/*疑惑点:题没有读懂,字典排序如果都是数字,类似于看组合的数字大小。
分析题目发现,就是找到最后一个数字 和从后往前第一个比它小的数字交换,然后对中间的数字进行排序。*/
}
//力扣代码
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
int r = len -1;
for (int i = len-1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int r1 = r; r1 >= 0 && r1 > i; r1--) {
if (nums <nums) {
int temp = nums;
nums = nums;
nums = temp;
Arrays.sort(nums,i+1,len );
return;
}
}
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
}
}
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
}
```
> 提交代码
```java
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
int r = len -1;
for (int i = len-1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int r1 = r; r1 >= 0 && r1 > i; r1--) {
if (nums <nums) {
int temp = nums;
nums = nums;
nums = temp;
Arrays.sort(nums,i+1,len );
return;
}
}
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
}
}
```
# 5 ✔ 最长公共子序列 Medium 2023-03-23 104
//给定两个字符串 text1 和 text2,返回这两个字符串的最长 公共子序列 的长度。如果不存在 公共子序列 ,返回 0 。
//
// 一个字符串的 子序列 是指这样一个新的字符串:它是由原字符串在不改变字符的相对顺序的情况下删除某些字符(也可以不删除任何字符)后组成的新字符串。
//
//
// 例如,"ace" 是 "abcde" 的子序列,但 "aec" 不是 "abcde" 的子序列。
//
//
// 两个字符串的 公共子序列 是这两个字符串所共同拥有的子序列。
//
//
//
// 示例 1:
//
//
//输入:text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace"
//输出:3
//解释:最长公共子序列是 "ace" ,它的长度为 3 。
//
//
// 示例 2:
//
//
//输入:text1 = "abc", text2 = "abc"
//输出:3
//解释:最长公共子序列是 "abc" ,它的长度为 3 。
//
//
// 示例 3:
//
//
//输入:text1 = "abc", text2 = "def"
//输出:0
//解释:两个字符串没有公共子序列,返回 0 。
//
//
//
//
// 提示:
//
//
// 1 <= text1.length, text2.length <= 1000
// text1 和 text2 仅由小写英文字符组成。
//
//
// Related Topics 字符串 动态规划 👍 1272 👎 0
---
`画图画图画图`
动态规划,感觉就是画表格就可以解决,我看到动态规划,直接画了一个方格,思路就清晰了。
给大家看看我画的图:
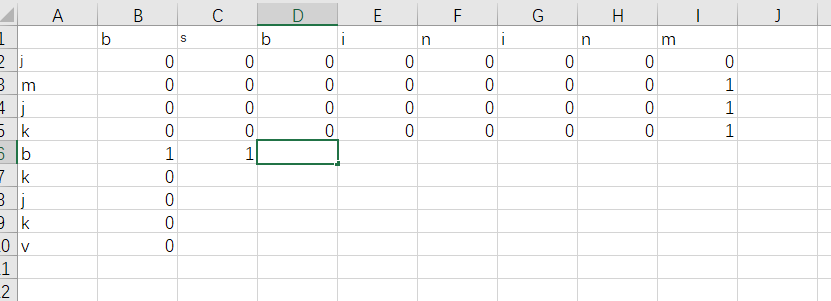
再巩固一下自己总结的解决动态规划的套路,分析原问题 =》 找子问题 =》确定子问题和原问题的关联 = 》 解决子问题 =》 解决原问题。
都是前几篇总结的规律呀,用上了,感觉不错哈哈。
>自测代码
```java
public class P1143_LongestCommonSubsequence{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试代码
Solution solution = new P1143_LongestCommonSubsequence().new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.longestCommonSubsequence("abcde", "ace"));
}
//力扣代码
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int len1 = text1.length();
int len2 = text2.length();
int[][] res = new int;
for (int i = 1; i < len1+1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < len2+1; j++) {
int max = Math.max(res, res);
if (text1.charAt(i-1) == text2.charAt(j-1)) {
max = Math.max(max,res + 1);
res = max;
}else {
max = Math.max(max,res);
res = max;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
}
```
> 提交代码
```java
class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int len1 = text1.length();
int len2 = text2.length();
int[][] res = new int;
for (int i = 1; i < len1+1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < len2+1; j++) {
int max = Math.max(res, res);
if (text1.charAt(i-1) == text2.charAt(j-1)) {
max = Math.max(max,res + 1);
res = max;
}else {
max = Math.max(max,res);
res = max;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
```
# 6 ✔ 两数相加 Medium 2023-03-22 102
//给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
//
// 请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
//
// 你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
//
//
//
// 示例 1:
//
//
//输入:l1 = , l2 =
//输出:
//解释:342 + 465 = 807.
//
//
// 示例 2:
//
//
//输入:l1 = , l2 =
//输出:
//
//
// 示例 3:
//
//
//输入:l1 = , l2 =
//输出:
//
//
//
//
// 提示:
//
//
// 每个链表中的节点数在范围 内
// 0 <= Node.val <= 9
// 题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
//
//
// Related Topics 递归 链表 数学 👍 9425 👎 0
---
>自测代码
```java
public class P2_AddTwoNumbers{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试代码
Solution solution = new P2_AddTwoNumbers().new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.addTwoNumbers(new ListNode(""), new ListNode("")).toString());
}
//力扣代码
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode dummyHead = head;
int temp = 0 ;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null){
int sum = l1.val + l2.val + temp;
dummyHead.next = new ListNode(sum%10);
temp = sum/10;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
while (l2 != null){
int sum =l2.val + temp;
dummyHead.next = new ListNode(sum%10);
temp = sum/10;
l2 = l2.next;
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
while (l1 != null){
int sum =l1.val + temp;
dummyHead.next = new ListNode(sum%10);
temp = sum/10;
l1 = l1.next;
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
if (temp != 0) {
dummyHead.next = new ListNode(temp);
}
return head.next;
}
}
```
> 提交代码
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode dummyHead = head;
int temp = 0 ;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null){
int sum = l1.val + l2.val + temp;
dummyHead.next = new ListNode(sum%10);
temp = sum/10;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
while (l2 != null){
int sum =l2.val + temp;
dummyHead.next = new ListNode(sum%10);
temp = sum/10;
l2 = l2.next;
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
while (l1 != null){
int sum =l1.val + temp;
dummyHead.next = new ListNode(sum%10);
temp = sum/10;
l1 = l1.next;
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
if (temp != 0) {
dummyHead.next = new ListNode(temp);
}
return head.next;
}
}
``` 感谢楼主,我算法很差,学习了 本帖最后由 chen110 于 2023-4-7 00:28 编辑
谢谢分享,支持楼主
页:
[1]