Il2cpp数据类型解析のC#String
本帖最后由 CIBao 于 2019-9-27 01:32 编辑> 修改游戏的前提是要去了解这个游戏, 虽然还是有很大一部分游戏公司对某些数据还是用基本数据类型, 但是精明的公司会自制新的类型来防止被直接修改, 本文这次带来的是C#的字符串解析
### 前言
C#的字符串生成可以通过hook il2cpp自带的new函数进行生成(使用方法参考本人的上一篇[文章](https://mihoyo.top/l2cpp-hook/))
```cpp
namespace il2cpp {
namespace vm {
class String {
...
static Il2CppString* New (const char* str);
...
};
} /* namespace vm */
} /* namespace il2cpp */
```
生成是轻松了, 但是解析就出大问题了, 涉及到大小端问题, 字节问题, 解析后出现的字节不对称问题, 简直要命
#### 相关文章
[冰鸽的开路教程](https://floe-ice.cn/archives/304)
(https://www.cnblogs.com/cthon/p/9297232.html)
#### 获取字节数组
通过冰鸽的教程, 可知C#内置的String是Unicode, 而我们linux则是utf-8
虽然一开始就打算使用内置的方法去获取对应的字节起始地址和字符数, 但是终究这种方法效率没直接硬核的对地址操作来得快, 所以还是用冰鸽开路留下来的结构体吧
```cpp
//C#字符串结构体仿制版
typedef struct CString
{
void *Empty;
void *WhiteChars;
int32_t length;
char start_char;
} CString;
```

#### 转换
接下来就是Unicode转UTF-8的环节了
看了一早上的相关介绍/说明文章, 头都要裂开了, 总结就是
- Unicode是保存字符的码值, 比如 **吗** 字, 码值为 **0x5417**
- 而UTF-8才是具体存放到内存中做交互的, **吗** 字在内存中是 **0x97 0x90 0xE5**
Unicode的占用还好是固定的2字节, 问题最大的就是UTF-8的文字字节并不是固定的, 英文字符只占一个字节, 汉字貌似都是3个字节吧
还好看到这篇(https://www.cnblogs.com/cthon/p/9297232.html), 这位大佬已经提供好了实现, 直接搬过来用就好了
```cpp
int unicode2UTF(long unic, char *pOutput)
{
if (unic >= 0xFFFF0000)
unic %= 0xFFFF0000;
if (unic <= 0x0000007F)
{
*pOutput = (unic & 0x7F);
return 1;
}
else if (unic >= 0x00000080 && unic <= 0x000007FF)
{
*(pOutput + 1) = (unic & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*pOutput = ((unic >> 6) & 0x1F) | 0xC0;
return 2;
}
else if (unic >= 0x00000800 && unic <= 0x0000FFFF)
{
*(pOutput + 2) = (unic & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 1) = ((unic >> 6) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*pOutput = ((unic >> 12) & 0x0F) | 0xE0;
return 3;
}
else if (unic >= 0x00010000 && unic <= 0x001FFFFF)
{
*(pOutput + 3) = (unic & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 2) = ((unic >> 6) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 1) = ((unic >> 12) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*pOutput = ((unic >> 18) & 0x07) | 0xF0;
return 4;
}
else if (unic >= 0x00200000 && unic <= 0x03FFFFFF)
{
*(pOutput + 4) = (unic & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 3) = ((unic >> 6) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 2) = ((unic >> 12) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 1) = ((unic >> 18) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*pOutput = ((unic >> 24) & 0x03) | 0xF8;
return 5;
}
else if (unic >= 0x04000000 && unic <= 0x7FFFFFFF)
{
*(pOutput + 5) = (unic & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 4) = ((unic >> 6) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 3) = ((unic >> 12) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 2) = ((unic >> 18) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*(pOutput + 1) = ((unic >> 24) & 0x3F) | 0x80;
*pOutput = ((unic >> 30) & 0x01) | 0xFC;
return 6;
}
return 0;
}
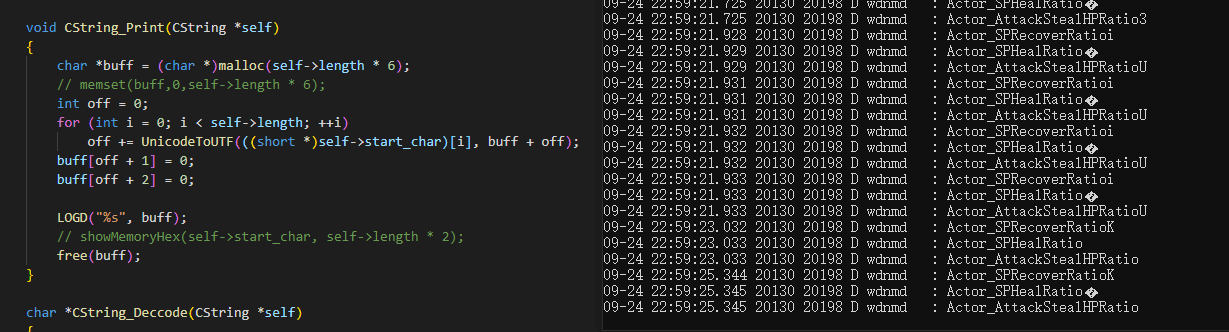
void CString_Print(CString *self)
{
char *buff = (char *)malloc(self->length * 6);
memset(buff,0,self->length * 6);
for (int i = 0, off = 0; i < self->length; ++i)
off += unicode2UTF(((short *)self->start_char), buff + off);
LOGD("%s", buff);
// showMemoryHex(self->start_char, self->length * 2);
free(buff);
}
```
虽然感觉有点浪费内存, 但是总比解析到一半, 缓冲区不够用重新扩充好~~(空间换时间, 最开始写的时候就很头大这个问题)~~
#### 踩坑
##### BUG1
测试解析的时候, 意外的发现, **草** 这个字符, Unicode编码为 **0x8349**
然后跑了一遍, 居然解析成字符 **I**, 我都傻了

将**unicode2UTF**函数的**unic**参数值打印出来一看更傻眼了

具体怎么产生这个BUG的问题还是没想出来, 有dalao知道的话请教一下小弟
解决方法是直接**抹除0xFFFFxxxx**, 取低字节两位完事 ~~好用完事, 出bug再说(逃~~
##### BUG2
本文的**CString_Print**函数其实还有另一个版本

直到前几天发现了神奇的状况, 一会乱码一会不乱码 ~~(偷懒不截全)~~
经过一顿猛如肥宅的操作后, 确认过unic也没问题, 就纳闷了怎么还会出现乱码呢
然后调整了一下结束符 **'\0'**
还是莫得用, 绝了
最后搬出 **memset** 大法
!(https://mihoyo.top/wp-content/uploads/il2cpp-decode-string-bug6.png)
虽然不知道发生了什么, 但是问题解决了
 可以先用 il2cpp_string_length 判断下长度
再用 il2cpp_string_chars取出.转换 #include "il2cpp_string.h"
#include <string.h>
std::string String::GetString(System_String_o *o)
{
System_String_Fields &fields = o->fields;
int32_t &m_stringLength = fields.m_stringLength;
uint16_t &m_firstChar = fields.m_firstChar;
std::u16string u16((char16_t *)&m_firstChar, 0, m_stringLength);
return utf16le_to_utf8(u16);
}
const char *String::GetChar(System_String_o *o)
{
return String::GetString(o).c_str();
}
System_String_o *String::ToString(const std::string &s)
{
System_String_o *o = new System_String_o();
System_String_Fields &fields = o->fields;
int32_t &m_stringLength = fields.m_stringLength;
uint16_t &m_firstChar = fields.m_firstChar;
m_stringLength = s.length();
std::u16string u16 = utf8_to_utf16le(s);
const char16_t *c = u16.c_str();
memcpy(&m_firstChar, c, m_stringLength * 2);
return o;
}
static inline uint16_t byteswap_ushort(uint16_t number) {
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER > 1310
return _byteswap_ushort(number);
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
return __builtin_bswap16(number);
#else
return (number >> 8) | (number << 8);
#endif
}
////////////////////////////////////////
// 以下转换都是在小端序下进行 //
////////////////////////////////////////
// 从UTF16编码字符串构建,需要带BOM标记
std::string utf16_to_utf8(const std::u16string &u16str) {
if (u16str.empty()) { return std::string(); }
//Byte Order Mark
char16_t bom = u16str;
switch (bom) {
case 0xFEFF: //Little Endian
return utf16le_to_utf8(u16str);
break;
case 0xFFFE: //Big Endian
return utf16be_to_utf8(u16str);
break;
default:
return std::string();
}
}
// 从UTF16 LE编码的字符串创建
std::string utf16le_to_utf8(const std::u16string &u16str) {
if (u16str.empty()) { return std::string(); }
const char16_t *p = u16str.data();
std::u16string::size_type len = u16str.length();
if (p == 0xFEFF) {
p += 1; //带有bom标记,后移
len -= 1;
}
// 开始转换
std::string u8str;
u8str.reserve(len * 3);
char16_t u16char;
for (std::u16string::size_type i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
// 这里假设是在小端序下(大端序不适用)
u16char = p;
// 1字节表示部分
if (u16char < 0x0080) {
// u16char <= 0x007f
// U- 0000 0000 ~ 0000 07ff : 0xxx xxxx
u8str.push_back((char) (u16char & 0x00FF));// 取低8bit
continue;
}
// 2 字节能表示部分
if (u16char >= 0x0080 && u16char <= 0x07FF) {
// * U-00000080 - U-000007FF:110xxxxx 10xxxxxx
u8str.push_back((char) (((u16char >> 6) & 0x1F) | 0xC0));
u8str.push_back((char) ((u16char & 0x3F) | 0x80));
continue;
}
// 代{过}{滤}理项对部分(4字节表示)
if (u16char >= 0xD800 && u16char <= 0xDBFF) {
// * U-00010000 - U-001FFFFF: 1111 0xxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx
uint32_t highSur = u16char;
uint32_t lowSur = p[++i];
// 从代{过}{滤}理项对到UNICODE代码点转换
// 1、从高代{过}{滤}理项减去0xD800,获取有效10bit
// 2、从低代{过}{滤}理项减去0xDC00,获取有效10bit
// 3、加上0x10000,获取UNICODE代码点值
uint32_t codePoint = highSur - 0xD800;
codePoint <<= 10;
codePoint |= lowSur - 0xDC00;
codePoint += 0x10000;
// 转为4字节UTF8编码表示
u8str.push_back((char) ((codePoint >> 18) | 0xF0));
u8str.push_back((char) (((codePoint >> 12) & 0x3F) | 0x80));
u8str.push_back((char) (((codePoint >> 06) & 0x3F) | 0x80));
u8str.push_back((char) ((codePoint & 0x3F) | 0x80));
continue;
}
// 3 字节表示部分
{
// * U-0000E000 - U-0000FFFF:1110xxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx
u8str.push_back((char) (((u16char >> 12) & 0x0F) | 0xE0));
u8str.push_back((char) (((u16char >> 6) & 0x3F) | 0x80));
u8str.push_back((char) ((u16char & 0x3F) | 0x80));
continue;
}
}
return u8str;
}
// 从UTF16BE编码字符串创建
std::string utf16be_to_utf8(const std::u16string &u16str) {
if (u16str.empty()) { return std::string(); }
const char16_t *p = u16str.data();
std::u16string::size_type len = u16str.length();
if (p == 0xFEFF) {
p += 1; //带有bom标记,后移
len -= 1;
}
// 开始转换
std::string u8str;
u8str.reserve(len * 2);
char16_t u16char; //u16le 低字节存低位,高字节存高位
for (std::u16string::size_type i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
// 这里假设是在小端序下(大端序不适用)
u16char = p;
// 将大端序转为小端序
u16char = byteswap_ushort(u16char);
// 1字节表示部分
if (u16char < 0x0080) {
// u16char <= 0x007f
// U- 0000 0000 ~ 0000 07ff : 0xxx xxxx
u8str.push_back((char) (u16char & 0x00FF));
continue;
}
// 2 字节能表示部分
if (u16char >= 0x0080 && u16char <= 0x07FF) {
// * U-00000080 - U-000007FF:110xxxxx 10xxxxxx
u8str.push_back((char) (((u16char >> 6) & 0x1F) | 0xC0));
u8str.push_back((char) ((u16char & 0x3F) | 0x80));
continue;
}
// 代{过}{滤}理项对部分(4字节表示)
if (u16char >= 0xD800 && u16char <= 0xDBFF) {
// * U-00010000 - U-001FFFFF: 1111 0xxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx
uint32_t highSur = u16char;
uint32_t lowSur = byteswap_ushort(p[++i]);
// 从代{过}{滤}理项对到UNICODE代码点转换
// 1、从高代{过}{滤}理项减去0xD800,获取有效10bit
// 2、从低代{过}{滤}理项减去0xDC00,获取有效10bit
// 3、加上0x10000,获取UNICODE代码点值
uint32_t codePoint = highSur - 0xD800;
codePoint <<= 10;
codePoint |= lowSur - 0xDC00;
codePoint += 0x10000;
// 转为4字节UTF8编码表示
u8str.push_back((char) ((codePoint >> 18) | 0xF0));
u8str.push_back((char) (((codePoint >> 12) & 0x3F) | 0x80));
u8str.push_back((char) (((codePoint >> 06) & 0x3F) | 0x80));
u8str.push_back((char) ((codePoint & 0x3F) | 0x80));
continue;
}
// 3 字节表示部分
{
// * U-0000E000 - U-0000FFFF:1110xxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx
u8str.push_back((char) (((u16char >> 12) & 0x0F) | 0xE0));
u8str.push_back((char) (((u16char >> 6) & 0x3F) | 0x80));
u8str.push_back((char) ((u16char & 0x3F) | 0x80));
continue;
}
}
return u8str;
}
// 获取转换为UTF-16 LE编码的字符串
std::u16string utf8_to_utf16le(const std::string &u8str, bool addbom, bool *ok) {
std::u16string u16str;
u16str.reserve(u8str.size());
if (addbom) {
u16str.push_back(0xFEFF); //bom (字节表示为 FF FE)
}
std::string::size_type len = u8str.length();
const unsigned char *p = (unsigned char *) (u8str.data());
// 判断是否具有BOM(判断长度小于3字节的情况)
if (len > 3 && p == 0xEF && p == 0xBB && p == 0xBF) {
p += 3;
len -= 3;
}
bool is_ok = true;
// 开始转换
for (std::string::size_type i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
uint32_t ch = p; // 取出UTF8序列首字节
if ((ch & 0x80) == 0) {
// 最高位为0,只有1字节表示UNICODE代码点
u16str.push_back((char16_t) ch);
continue;
}
switch (ch & 0xF0) {
case 0xF0: // 4 字节字符, 0x10000 到 0x10FFFF
{
uint32_t c2 = p[++i];
uint32_t c3 = p[++i];
uint32_t c4 = p[++i];
// 计算UNICODE代码点值(第一个字节取低3bit,其余取6bit)
uint32_t codePoint =
((ch & 0x07U) << 18) | ((c2 & 0x3FU) << 12) | ((c3 & 0x3FU) << 6) |
(c4 & 0x3FU);
if (codePoint >= 0x10000) {
// 在UTF-16中 U+10000 到 U+10FFFF 用两个16bit单元表示, 代{过}{滤}理项对.
// 1、将代码点减去0x10000(得到长度为20bit的值)
// 2、high 代{过}{滤}理项 是将那20bit中的高10bit加上0xD800(110110 00 00000000)
// 3、low代{过}{滤}理项 是将那20bit中的低10bit加上0xDC00(110111 00 00000000)
codePoint -= 0x10000;
u16str.push_back((char16_t) ((codePoint >> 10) | 0xD800U));
u16str.push_back((char16_t) ((codePoint & 0x03FFU) | 0xDC00U));
} else {
// 在UTF-16中 U+0000 到 U+D7FF 以及 U+E000 到 U+FFFF 与Unicode代码点值相同.
// U+D800 到 U+DFFF 是无效字符, 为了简单起见,这里假设它不存在(如果有则不编码)
u16str.push_back((char16_t) codePoint);
}
}
break;
case 0xE0: // 3 字节字符, 0x800 到 0xFFFF
{
uint32_t c2 = p[++i];
uint32_t c3 = p[++i];
// 计算UNICODE代码点值(第一个字节取低4bit,其余取6bit)
uint32_t codePoint = ((ch & 0x0FU) << 12) | ((c2 & 0x3FU) << 6) | (c3 & 0x3FU);
u16str.push_back((char16_t) codePoint);
}
break;
case 0xD0: // 2 字节字符, 0x80 到 0x7FF
case 0xC0: {
uint32_t c2 = p[++i];
// 计算UNICODE代码点值(第一个字节取低5bit,其余取6bit)
uint32_t codePoint = ((ch & 0x1FU) << 12) | ((c2 & 0x3FU) << 6);
u16str.push_back((char16_t) codePoint);
}
break;
default: // 单字节部分(前面已经处理,所以不应该进来)
is_ok = false;
break;
}
}
if (ok != NULL) { *ok = is_ok; }
return u16str;
}
// 获取转换为UTF-16 BE的字符串
std::u16string utf8_to_utf16be(const std::string &u8str, bool addbom, bool *ok) {
// 先获取utf16le编码字符串
std::u16string u16str = utf8_to_utf16le(u8str, addbom, ok);
// 将小端序转换为大端序
for (size_t i = 0; i < u16str.size(); ++i) {
u16str = byteswap_ushort(u16str);
}
return u16str;
}
感谢楼主无私的奉献。。。。。。。。。。。。。 猛如肥宅是什么操作,你们一个个口口声声说自己是肥宅实际一个比一个dalao。 战术瞪眼啊!! meiercn 发表于 2019-9-27 07:29
可以先用 il2cpp_string_length 判断下长度
再用 il2cpp_string_chars取出.转换
对, 不过结构体更暴力点, 那些方法实际上也就是用self+偏移获取指定的成员函数, 使用结构体还能省去一部分函数的开销 打印的时候我是用frida读偏移地址的UTF16字符串的 感谢分享
既然已经不涉及我的利益了,就让我来告诉你一个简单地办法吧 Java用的是Unicode,native用的是utf-8,所以我们完全可以直接利用Jni完成转换工作
页:
[1]
2