更新
简易Android ARM&ARM64 GOT Hook (二)
基本思路为:基于执行视图,解析内存中的ELF,查找导入符号并替换函数地址
概述
本文以Hook公共库libc.so的getpid函数为例,基于ELF的链接视图(Linking View),讨论Android ARM&ARM64架构的GOT/PLT Hook。
原理
程序加载后,在执行之前,需要先进行动态链接,并进行重定位。
调用外部函数时,需要先跳转到PLT(Procedure Link Table 程序链接表,位于代码段),再跳转到GOT(Global Offset Table 全局偏移表,位于数据段),执行目标函数。
延迟绑定(Lazy Binding):当外部函数被调用时,才进行地址解析和重定位
由于Android ARM架构不支持延迟绑定,在linker重定位后,GOT已被填充为内存地址 (可使用IDA动态调试验证)
因此,可以通过比对函数地址,修改指定模块的对应GOT表项,实现对外部导入函数的Hook
具体思路
编写so库,在so加载的构造函数(linker会主动调用)中完成以下操作:定位目标模块基址、基于链接视图解析ELF文件,得到GOT表地址及大小、遍历GOT表替换目标函数地址。
注入方式
使用LIEF修改ELF文件,导入该动态库。
编译环境
Android Studio 2020.3.1、Gradle 7.0.1、CMake 3.18.1、NDK 23.0.7599858
ABI: armeabi-v7a,arm64-v8a
PS:其实也可以脱离Android Studio手动编译,见使用CMake交叉编译Android ARM程序
编码
使用Android Studio创建Native C++项目,然后增加两个Android Native Library模块,分别命名为victim和inject
待注入程序
victim.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("my pid: %d\n", getpid());
// getchar();
return 0;
}
调用getpid获取进程id(IDA动态调试时使用getchar,方便查看内存)
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.18.1)
project(victim)
add_executable(victim victim.cpp)
编译为可执行文件
注入动态库
// 基于链接视图解析ELF
uintptr_t hackBySection(const char *moudle_path, const char *target_lib, const char *target_func,
uintptr_t replace) {
LOGI("hack start.\n");
// 获取目标函数地址
void *handle = dlopen(target_lib, RTLD_LAZY);
auto ori = (uintptr_t) dlsym(handle, target_func);
LOGI("hack ori addr: %lX\n", ori);
int GOTSize = 0;
// 获取GOT表地址及大小 (解析Section)
uintptr_t GOTBase = getGOTBase(GOTSize, moudle_path);
// 遍历GOT表,查找符号地址
uintptr_t replaceAddr = getSymAddrInGOT(GOTBase, GOTSize, ori);
// 替换地址
replaceFunction(replaceAddr, replace, ori);
return ori;
}
// 原方法的备份
int (*getpidOri)();
// 替换方法
int getpidReplace() {
LOGI("before hook getpid\n");
//调用原方法
int pid = (int) getpidOri();
LOGI("after hook getpid: %d\n", pid);
return 233333;
}
//so加载时由linker调用
void __attribute__((constructor)) init() {
uintptr_t ori = hackBySection(MODULE_PATH, "libc.so", "getpid",
(uintptr_t) getpidReplace);
getpidOri = (int (*)()) (ori);
}
注意:Android 7.0以上,dlopen只能加载公共库,加载非公共库需要绕过命名空间限制。
子函数
获取模块基址
uintptr_t getModuleBase(const char *modulePath) {
uintptr_t addr = 0;
char buff[256] = "\n";
FILE * fp = fopen("/proc/self/maps", "r");
while (fgets(buff, sizeof(buff), fp)) {
if (strstr(buff, "r-xp") && strstr(buff, modulePath) &&
sscanf(buff, "%lx", &addr) == 1)
break;
}
fclose(fp);
return addr;
}
遍历/proc/self/maps文件内容,根据权限及模块路径找到基址。
获取GOT表地址及其大小
篇幅所限,此处仅给出思路(以ARM为例),完整代码见AndroidGotHook
根据模块路径打开ELF文件(本例为/data/local/tmp/victim-patch-arm),解析ELF文件结构(图片为010Editor ELF模板解析结果):
首先从elf header中得到section header table的起始偏移(e_shoff)、字符串表索引(e_shstrndx)、section header大小(e_shentsize)和总section header个数(e_shnum)
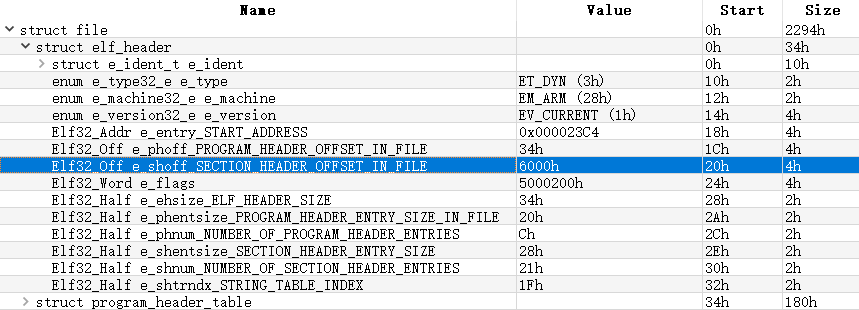
然后计算出字符串表section header的偏移地址(e_shoff + e_shstrndx * e_shentsize),从而得到字符串表的偏移值(s_offset)及大小(s_size)
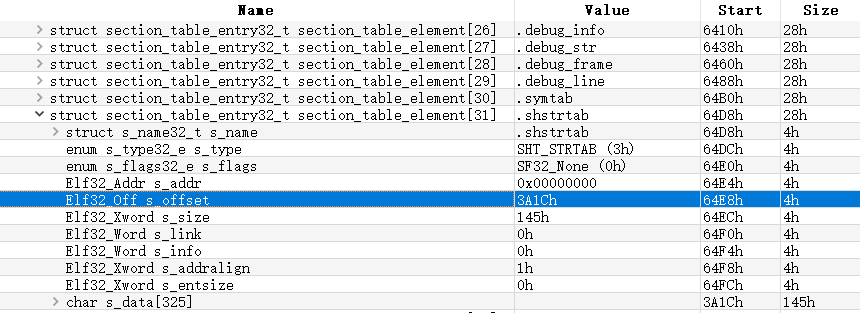
再遍历section header table,查找sh_type为SHT_PROGBITS 且 section名(通过sh_name查询字符串表)为.got的section header,得到GOT表偏移值(s_offset)及大小(s_size)
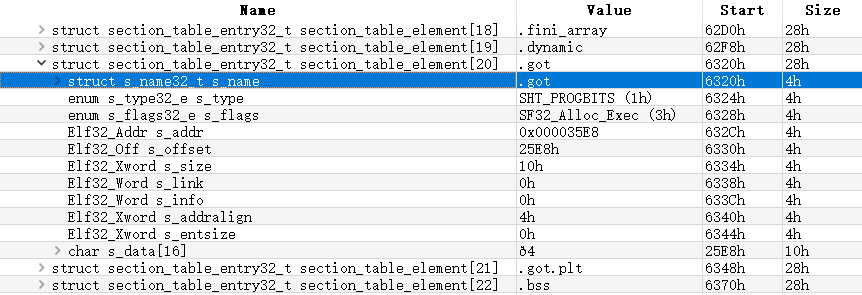
最终将GOT表偏移值与模块基址相加,得到GOT表地址。
查找目标函数地址
uintptr_t getSymAddrInGOT(uintptr_t GOTBase, int GOTSize, uintptr_t ori) {
if (GOTBase == 0) {
LOGI("getSymAddrInGOT failed! addr [%lX] is wrong\n", GOTBase);
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < GOTSize; ++i) {
uintptr_t addr = GOTBase + i * 4;
uintptr_t item = *(uintptr_t *) (addr);
// LOGI("GOT [%d]: %lX\n", i, item);
if (item == ori) {
return addr;
}
}
LOGI("getSymAddrInGOT %lX not found!\n", ori);
return 0;
}
遍历GOT表,查找目标函数地址。
替换函数地址
void replaceFunction(uintptr_t addr, uintptr_t replace, uintptr_t ori) {
if (addr == 0) {
LOGI("replace failed! addr is wrong\n");
return;
}
// 比对函数地址
uintptr_t item = *(uintptr_t *) (addr);
if (item == replace) {
LOGI("function has been replaced!\n");
return;
}
if (item != ori) {
LOGI("replace failed! unexpected function address %X\n", item);
return;
}
//修改权限、替换地址、清空指令缓存
LOGI("replace %X to %X\n", ori, replace);
mprotect((void *) PAGE_START(addr), PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE);
*(uintptr_t *) addr = replace;
__builtin___clear_cache((char *) PAGE_START(addr), (char *) PAGE_END(addr));
}
首先判断函数是否已被替换,然后与期望值相比较,如果一致,则进行以下操作:
将该地址权限设置为可读可写,然后替换函数地址,并清空指令缓存。
适配ARM64
添加宏,将Elf32_w替换为ELFW(w):
#if defined(__LP64__)
#define ELFW(what) Elf64_ ## what
#else
#define ELFW(what) Elf32_ ## what
#endif
根据架构使用不同的路径:
#if defined(__LP64__)
#define MODULE_PATH "/data/local/tmp/victim-patch-arm64"
#else
#define MODULE_PATH "/data/local/tmp/victim-patch-arm"
#endif
使用LIEF添加依赖
编译完成后,打开victim/build/intermediates/cmake/debug/obj/CPU架构/,使用LIEF注入victim
import lief,sys
abi = "armeabi-v7a"
tail = "-arm"
if(len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "arm64-v8a"):
abi = sys.argv[1]
tail = "-arm64"
path = "../victim/build/intermediates/cmake/debug/obj/"+abi+"/victim"
elf = lief.parse(path)
elf.add_library("/data/local/tmp/libinject"+tail+".so")
elf.write("victim-patch"+tail)
print("patch success")
测试
打开inject/build/intermediates/cmake/debug/obj/CPU架构/,
使用adb将生成的libinject.so和victim-patch-arm发送到手机的/data/local/tmp/目录(so需要重命名)
adb push libinject.so /data/local/tmp/libinject-arm.so
adb push victim-patch-arm /data/local/tmp
设置可执行权限后,运行victim-patch-arm
adb shell chmod +x /data/local/tmp/victim-patch-arm
adb shell /data/local/tmp/victim-patch-arm
(ARM64同理)
运行结果
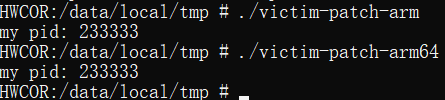
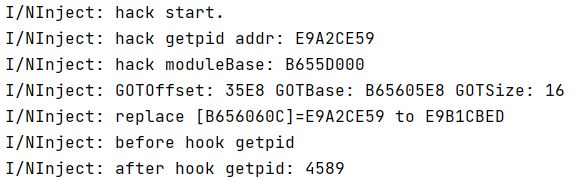
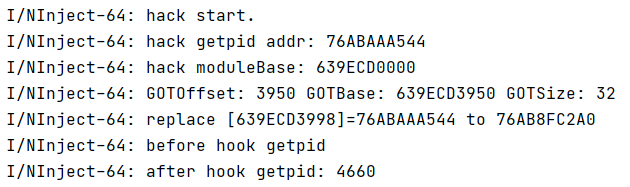
成功实现对getpid函数的GOT Hook。
日志
ARM
ARM64
存在的问题
- 未绕过
dlopen命名空间限制,在Android 7以上无法打开非公共库
- 未hook
dlopen,无法实时修改加载模块的GOT表
- 解析maps获取模块基址,兼容性可能存在一定问题
- 基于链接视图静态解析ELF,无法处理加壳的so
- 静态注入可执行文件,无法绕过完整性检测
- 未提供卸载函数,无法恢复GOT表
- 模块路径硬编码,通用性不足
- ...
总结
通过本项目,学习了GOT Hook原理和ELF文件结构,并适配了ARM64架构,目的基本达到。虽然功能还不够完善,但短期内应该不会再改动了(俗话说得好:不要重复造轮子)。
实际应用可以考虑使用字节的bhook
参考
android中基于plt/got的hook实现原理
聊聊Linux动态链接中的PLT和GOT(2)——延迟重定位
constructor属性函数在动态库加载中的执行顺序
Android7.0以上命名空间详解(dlopen限制)
Android中GOT表HOOK手动实现
Android GOT Hook

 发表于 2021-8-24 09:57
发表于 2021-8-24 09:57
 发表于 2021-8-24 11:08
发表于 2021-8-24 11:08
 发表于 2021-8-24 12:12
发表于 2021-8-24 12:12
 发表于 2021-8-24 21:10
发表于 2021-8-24 21:10
 发表于 2021-8-25 15:15
发表于 2021-8-25 15:15
 发表于 2021-8-27 09:43
发表于 2021-8-27 09:43
 发表于 2021-8-29 07:34
发表于 2021-8-29 07:34
 发表于 2021-8-29 08:56
发表于 2021-8-29 08:56